
Boilers &
Hydronic Heating
What is Hydronic Heating?
A boiler is a closed vessel in which water or other fluid is heated. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.
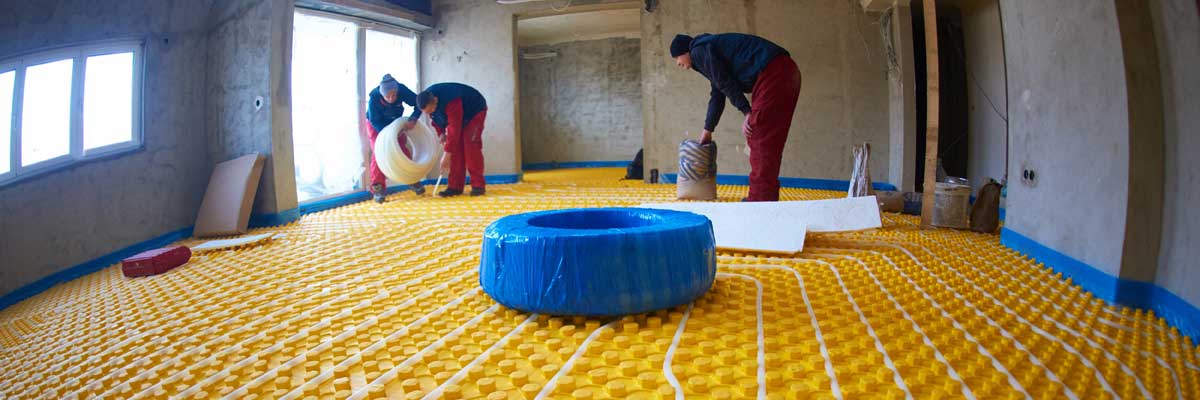
Hydronic heating is a type of central heating system that uses a boiler to heat water, which is then circulated through a network of pipes to radiators or other heat emitters in the rooms of a building. The radiators or heat emitters then transfer the heat from the hot water to the air in the room, warming the space. Hydronic heating systems are highly efficient and can be powered by a variety of fuels, including natural gas, propane, oil, and electricity.
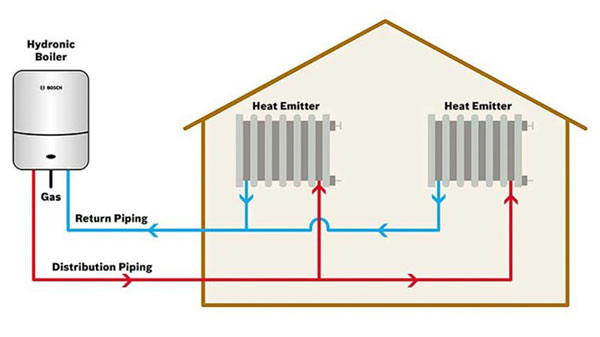
Hydronic heating is used to provide central heating for buildings such as homes, apartment complexes, offices, and other structures. It is used in such applications as radiant floor systems, located in various rooms of the building. This transfer of heat warms the air in the rooms, providing a comfortable living or working environment.
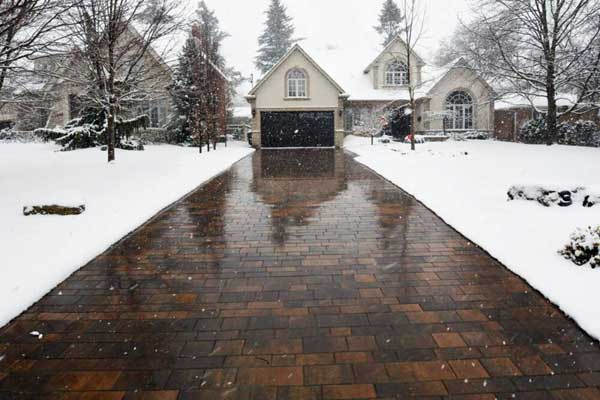
Hydronic heating can also be used for other purposes such as providing hot water for showers, sinks, and other fixtures, and even to heat swimming pools or provide snow and ice melting in driveways and sidewalks.
The efficiency and flexibility of hydronic heating make it a popular choice for many types of uses.
What are the advantages of hydronic heating over traditional forced-air systems?
Hydronic heating systems have several advantages over traditional forced-air systems:

Contact Sharpe Advantage to discuss the use of hydronic heating in your home
Heating Service Areas
We provide heating services throughout Durham Region and the Greater Toronto Area:
- Oshawa – Furnace and heating services
- Whitby – Complete HVAC services
- Richmond Hill – Heating specialists
- Toronto & GTA – Full service area
Call 905-441-5466 for heating service in your area.

